In the knockout stage of new energy vehicle enterprises, Xiaomi’s "high-profile" entry into new energy vehicles has brought a lot of shock to the automobile industry. Since the technical conference, the hot topic of Xiaomi Auto has been constant, and the market is expected to be full, but it is also trapped in various disputes. At present, the official press conference will usher in a countdown, and facing the real market test, Xiaomi Automobile will usher in a new round of public opinion risk impact.
Author Miao Jian Research Institute
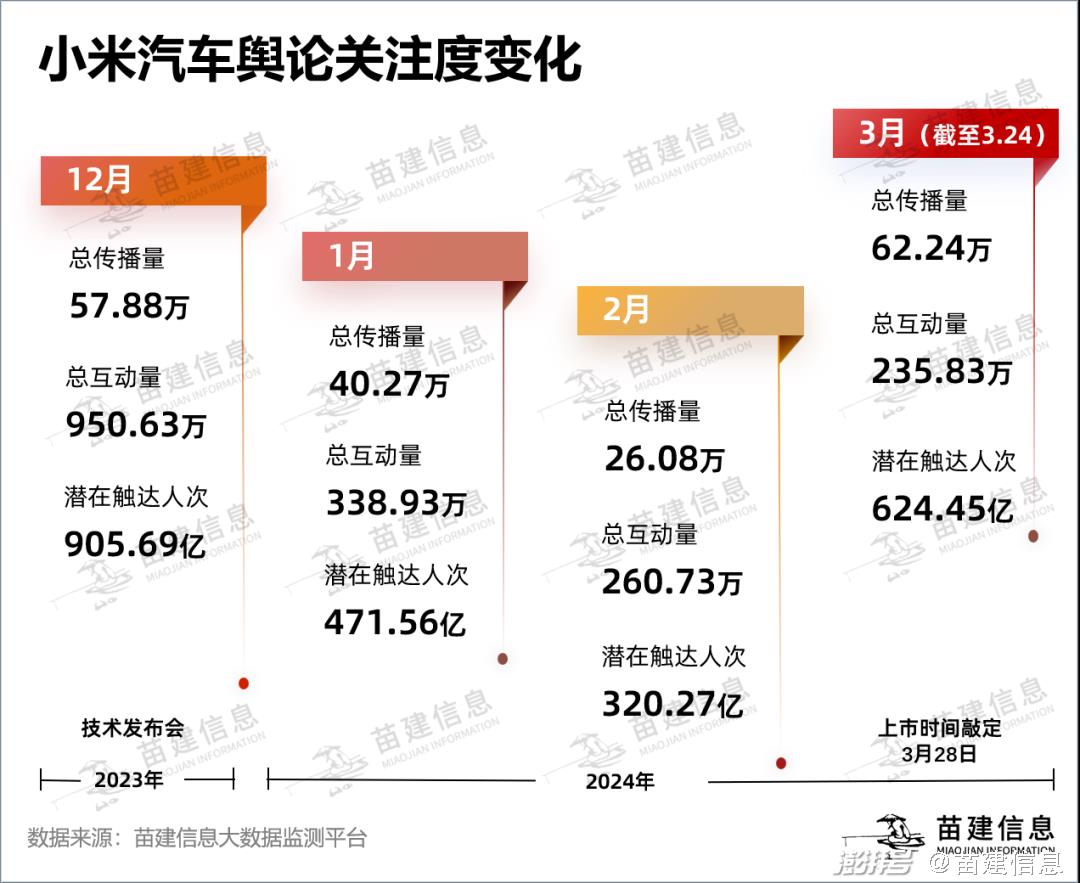
According to the data of Miaojian Information Big Data Monitoring Platform, from December 25th, 2023 to March 24th, 2024, 1,699,200 items related to "Xiaomi Auto" and "Xiaomi SU7" have spread across the whole network, and related topics have been listed on the hot search lists of 12 platforms including Tik Tok, Weibo and Baidu, with a total of more than 230 times, and the cumulative time on the list has exceeded 1,400 hours.
Miao Jian information analysis found that
In the "price war" period, coupled with the brand impression of "high cost performance", XIAOMI SU7, the first+first Xiaomi car, has a high degree of attention, and the public opinion has crushed all other single-brand models for three months.
The topic of price runs through the warm-up period of products. Compared with design and technical topics, price is still the most concerned topic of public opinion before the products in the automobile industry go on the market.
In 3 months, there were 319 articles related to SU7, with an average of 3.5 articles published every day. Lei Jun continued to speak out through official micro by virtue of his personal influence, which played an important leading role in the overall topic communication. Timely dispel rumors, disclose important information and respond to public concerns, constantly create and form hot topics, and maintain product popularity.
On March 28th, Xiaomi SU7 will be officially released at the listing conference, and the risk window of Xiaomi Auto’s public opinion will be reopened soon. After the product is officially listed, the risk of public opinion around the final pricing combined with test drive, comparative evaluation, marketing, sales delivery, new car problems, accidents and so on will continue to rise.
01
Sorting out the main communication threads of Xiaomi SU7 before listing.
On November 15th, 2023, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the Announcement of Road Motor Vehicle Manufacturers and Products (the 377th batch) and the Catalogue of Energy-saving and New Energy-using Vehicles with Vehicle and Vessel Tax Relief (the 56th batch), in which Xiaomi Automobile is located.
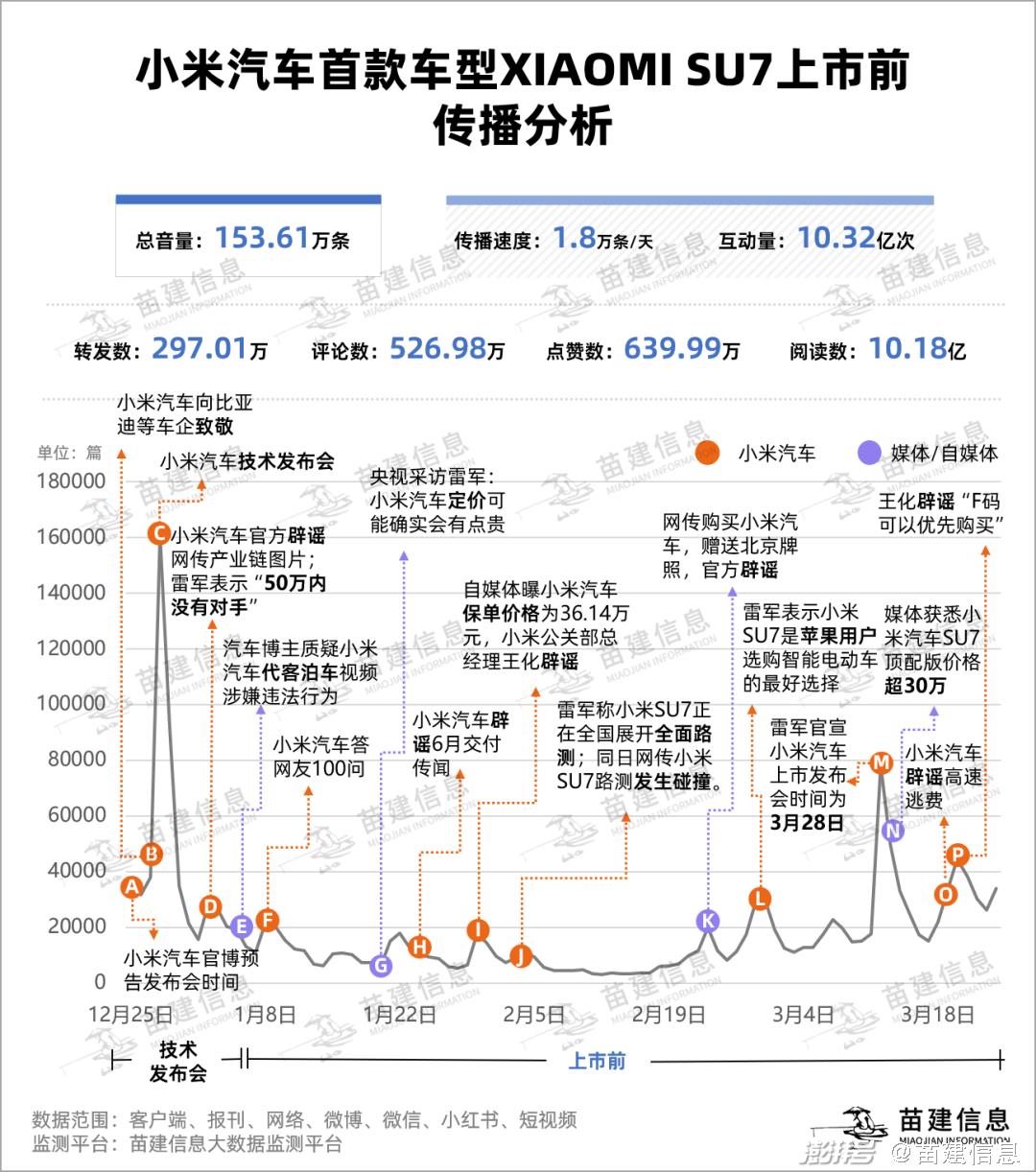
The recent major communication/public opinion events of "Xiaomi Automobile" are as follows:
A On December 25th, 2023, the official blog of Xiaomi Automobile announced that the "Xiaomi Automobile Technology Conference" would be held on December 28th, and Xiaomi officially revealed the relevant information of Xiaomi Automobile for the first time.
B On December 27th, 2023, Lei Jun released a message in his personal Weibo, paying tribute to the pioneers of new energy vehicles in China, such as BYD and Weilai. That night, Xiaomi Automobile paid a grand tribute to Huawei, Tucki, Ideality, BYD and Weilai through outdoor billboards.
C On December 28th, 2023, Xiaomi Automobile held a technical conference. Lei Jun said at the Xiaomi Automobile Technology Conference: "So don’t shout 99,000, it’s impossible." "Anyone who has this kind of performance and configuration will get more than 400,000 yuan, so there is no need to talk about 149,000 yuan, or we should respect technology."
D On January 2, 2024, a spokesman for @ Xiaomi Company wrote a rumor: We recently paid attention to a picture about Xiaomi’s automobile industry chain. After verification, at least 50% of the contents were completely wrong. It said that the information summary of the "industrial chain" pictures is full of loopholes and misleading to the public and investors, which is deeply puzzled.

On the same day, some netizens discussed the price of SU7 under Lei Jun Weibo. Lei Jun said: "Is there an opponent within 500,000?" . This reply triggered speculation that the final price of SU7 may be between 200,000 and 500,000 yuan.
E On January 5th, 2024, the car blogger "Li Sir Jiaolu" released Weibo news, questioning the suspected illegal behavior of Xiaomi Auto parking service video, and its comments questioned the blogger’s double standard.
F On January 8 -10, 2024, Xiaomi Automobile released "Answering 100 Questions from Netizens" in batches.
G On January 20, 2024, Lei Jun said in an interview with CCTV: "It is expected to be officially listed in the first half of 2024, and now it is undergoing small-scale mass production. This car has a very strong configuration and a very high cost. I think everyone is joking when they shout 99,000 yuan, 149,000 yuan or even 199,000 yuan. Pricing may indeed be a bit expensive, and we will announce it at the official product launch conference of Xiaomi Automobile. "
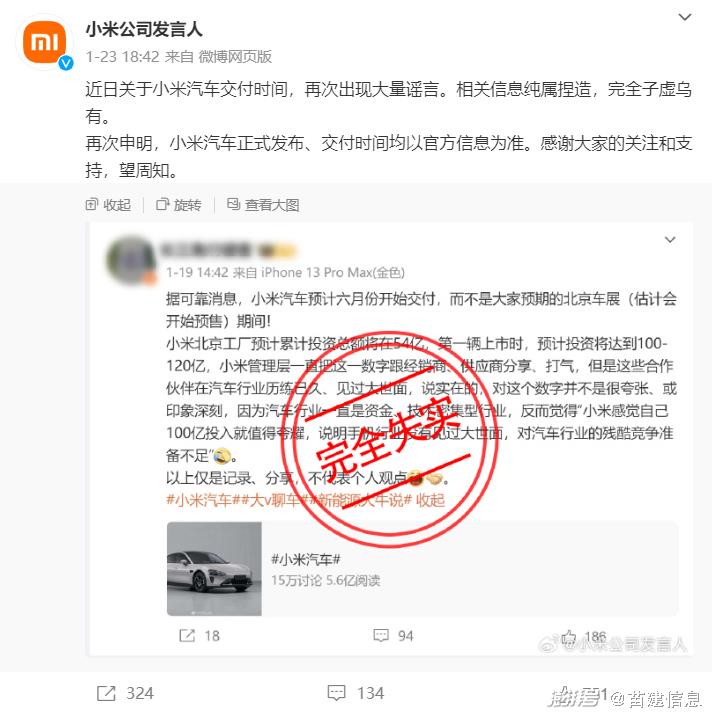
H On January 23rd, 2024, a spokesman for @ Xiaomi Company issued a document in Weibo to refute the rumor that Xiaomi Automobile was delivered in June. Recently, there have been a lot of rumors about the delivery time of Xiaomi Automobile. The relevant information is pure fabrication, completely false. Once again, the official release and delivery time of Xiaomi Automobile are subject to official information.
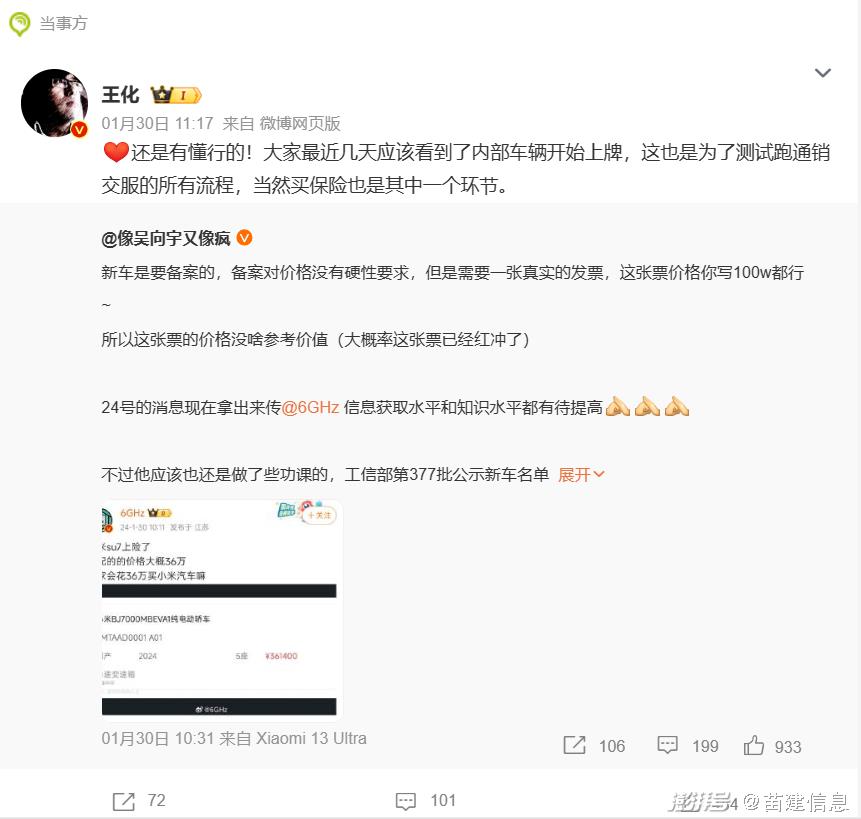
I On January 30th, 2024, Wang Hua, general manager of Xiaomi’s public relations department, responded to the issue of # Xiaomi’s policy price exposure # in Weibo, saying that in recent days, everyone should have seen the internal vehicles start to be licensed, which is also to test all the processes of running through the sales and delivery, and of course, buying insurance is also one of the links.
J On February 3, 2024, Lei Jun announced in Weibo that Xiaomi SU7 was conducting a comprehensive road test nationwide to make final preparations for the listing of Xiaomi SU7, and would focus more on the automobile business.
K On February 23, 2024, it was reported that Xiaomi’s early employees close to Lei Jun revealed that "Lei Jun is making a big move. The first car owners who buy Xiaomi cars may give them licenses if they don’t have a Beijing license." In response, a spokesperson for @ Xiaomi Company responded that it was completely inaccurate. Xiaomi’s pricing, delivery and sales policies are subject to the official release, which is well known.
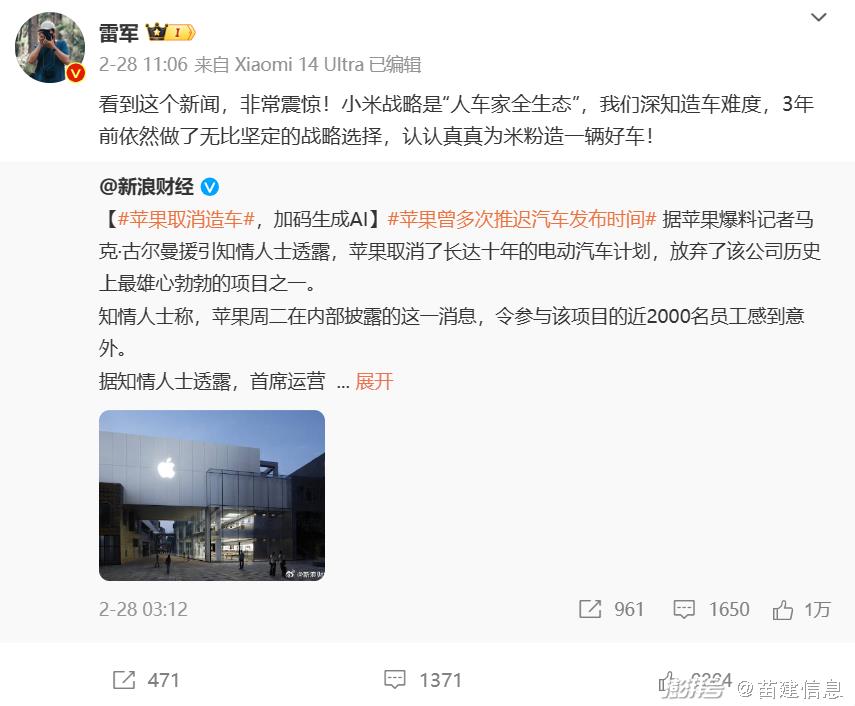
On February 28th, 2024, Lei Jun voiced "Apple canceled making cars" and said that "Apple users will definitely be the best choice when purchasing smart electric cars".
M On March 12, 2024, Lei Jun released the official announcement of Xiaomi Automobile in Weibo on March 28.
N On March 13th, 2024, the reporter of science and technology innovation board Daily learned from the sales channel of Xiaomi Automobile that the price of SU7 top distribution will exceed that of M5 top distribution (about 300,000 yuan).
O On March 19th, 2024, a spokesperson of @ Xiaomi Company issued a rumor, saying that the Xiaomi road test vehicle was closed-loop tested on the closed-loop expressway, and there were no violations such as high-speed illegal U-turn, speeding, and escaping high-speed tolls.
P On March 20th, 2024, Wang Hua, general manager of Xiaomi Public Relations Department, denied that "Xiaomi Automobile will issue 1000 Xiaomi SU7F codes". "As far as I know, there is no channel for priority purchase of F codes".
02
Public opinion concerns
According to the monitoring results of Miaojian Information Big Data Platform, price is the most concerned topic of public opinion. Among them, the discussion of Xiaomi automobile product itself mainly focuses on price, technology and design.
I. Price
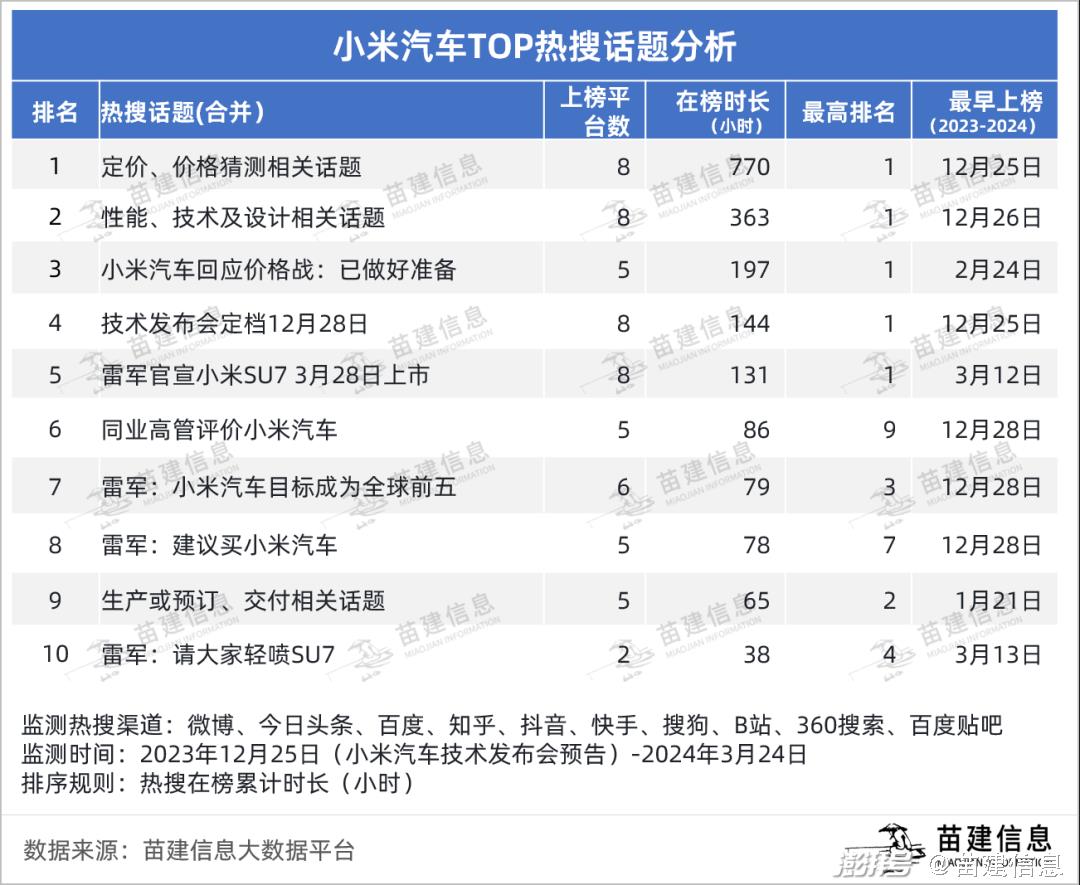
In the technical conference and CCTV interview, Lei Jun repeatedly said "Don’t shout 99,000, it’s impossible", "Anyone with this performance and configuration will have to pay more than 400,000, so there is no need to talk about 149,000", "The price is really a bit expensive, and 199,000 is impossible", and he even replied in Weibo "Is there an opponent within 500,000?"
The "cost-effective" label of Xiaomi’s mobile phone is deeply rooted in people’s hearts, which makes Xiaomi’s car trapped by the public opinion of "low price" and "low end" before its release. From the media point of view, Xiaomi held this technical conference just to break the existing public opinion situation, and wanted to tell everyone that "we still have to respect science and technology".
On January 5th, Wang Hua, general manager of Xiaomi’s public relations department, released the ultimate rumor about Xiaomi Automobile in Weibo: until the end of the official Xiaomi Automobile product launch conference, all the information and posters with the version and price of Xiaomi Automobile were false. On January 8th and 9th, Lei Jun Weibo released Xiaomi Auto to answer 100 questions from netizens, and also officially answered questions about pricing.



On February 21st, the price of # Xiaomi Auto was searched again in Weibo, and some cars said from the media that "the current situation is even more complicated". On March 6th, Li Guoqing, the founder of Dangdang, sent a video calling Lei Jun, asking Lei Jun to price Xiaomi for 150,000 to 200,000 yuan. On March 13th, the media learned that the price of SU7 top plate will exceed that of M5 top plate (about 300,000 yuan).
The release of technology, the voice of executives, the pressure from inside and outside the industry, and the wind of prices continue. The car industry is in a big environment of "low price". Faced with the expectation of many "rice noodles", Xiaomi will insist on going upstream and entering the mid-to high-end market in pricing, or push up the consumer’s budget through marketing and kill at a low price. The continuous price topic and various speculations will make Xiaomi SU7 in the preheating stage occupy the public opinion field in the car industry.
Mainstream media: The participating media are mainly financial media such as Caijing. com, national business daily and China Business News, mainly to report the latest development of Xiaomi Automobile and the contents of senior executives’ speeches, with few media comments.
Professionals: Guess why Xiaomi Auto has not announced its pricing.
According to national business daily, Pang Rui, a well-known brand expert and founding partner of Zhansheng Communication, "So far, regarding the pricing of Xiaomi SU7, Xiaomi is mostly denying the price circulated on the Internet, without giving any positive hints. Perhaps this is also a pricing test strategy, that is, by observing the market’s public opinion feedback on different rumored prices, Xiaomi can constantly correct the price and gradually form the final pricing in the process. "
According to China Net Finance, Liang Zhenpeng, a senior industrial economic observer, believes that "on the one hand, it takes a long time for a car to go from PPT to commercial mass production, and then to improve the yield to meet the standards of product quality, process performance and other technical parameters. For Xiaomi, the cost is difficult to determine for the time being, so the price has not been disclosed yet; On the other hand, in the process of R&D and manufacturing, Xiaomi’s automobile products will continue to be iteratively updated, and the cost will continue to change, thus affecting the final pricing. "
From the media: initiate pricing speculation discussion and analyze the situation of Xiaomi SU7 according to the actions of other car companies.
Weibo-Bigu: I feel that BYD’s price reduction can kill everything. Not all of Gaohe has fallen, and Wei Xiaoli has a hard time. If BYD starts to enlarge its recruitment further, Xiaomi will be miserable.
Weibo-_-Second Senior Brother: BYD took the lead in killing the red eye within 100,000 yuan, and extremely krypton Tucki pulled the 800V to within 200,000 yuan. Therefore, the 400V single motor introduced by Xiaomi SU7 does not have the version of lidar. Once it exceeds 200,000, it will be difficult to be a new brand. Xiaomi has only one chance to play cards.
Netizen: ridicule pricing, discuss the price in mind, think about marketing routines, and discuss price reduction issues.
First, throw a confusing 300,000 yuan to the outside world, and blow the wind. When the listing is low, it will be set at more than 20, and then the whole network will say that it is cheap and buy buy will buy it.
The marketing gimmick is full, just don’t know if the final price will satisfy the public.
Almost. Aren’t you tired of this old routine?
Rumor? I think this is what Lei Jun wants. All the way from Xiaomi mobile phone is a similar eye-catching strategy.
The price was not announced at the press conference. By understanding how much users are willing to pay for Xiaomi Automobile, pricing is made according to this price.
If it’s so expensive, you can only wait for Redmi car; As expected, it may be accepted that there are so many piles of materials at the technical conference.
Didn’t a lot of news say 500 thousand before, and now another 360 thousand, I think it’s better to wait for the press conference
BYD’s 200,000 cars haven’t been reduced in price, so we can sell them at whatever crowd we target. If BYD drops another 10,000, we will buy them from people within 100,000.
It has been delayed for too long, and there is no enthusiasm for attention.
Second, technology
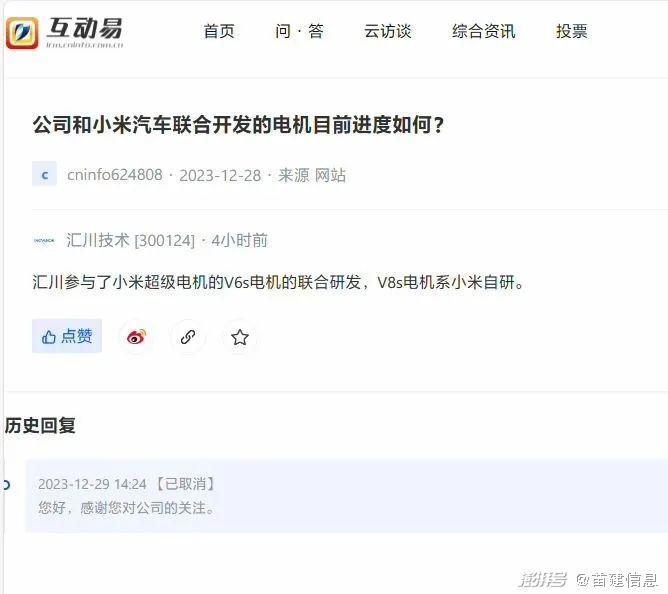
Under the public opinion environment that new energy car companies generally bear the original crime of technology, the louder the slogan of "self-research" is shouted, the more attention and condemnation it attracts. Lei Jun publicized "self-research" for many times at the press conference. Later, due to the constant controversy over "self-research", the rumors mainly focused on Xiaomi V8s super motor and Xiaomi Titan alloy, and thought that Xiaomi Automobile was just an assembly plant.
These false information have been rumored one after another. On the night of the press conference, there was a voice that Xiaomi V8s super motor was from Huichuan technology, not self-developed. Huichuan technology immediately responded to "V8s motor is self-developed by Xiaomi" on the stock trading platform, but some netizens still said, "Is Xiaomi fully self-developed? How did Huichuan know?"
In addition, the Titan alloy developed by Xiaomi was thought to be plagiarized by a university teacher, and then the teacher responded that "the ingredients were wrong, and Xiaomi did develop it himself".
A picture of Xiaomi automobile industry chain was also exposed on the Internet, which shows that most parts of Xiaomi automobile are supplied by third parties. In this regard, Xiaomi Automobile denies that at least 50% of the contents are completely wrong.
Since the media: Based on the information released by the government, this paper analyzes the five major technologies of Xiaomi Automobile and whether it is "self-developed". The overall tonality of the public opinion field is neutral.
Wechat-Zinc Scale: An industry insider told Zinc Scale, "This is the same as satirizing that the large aircraft C919 is’ assembled goods’, either ignorant or with ulterior motives. The key lies in how many core technologies are mastered, not how many parts are mastered. For example, the large die-casting equipment comes from a third-party supplier, but the large die-casting equipment cluster system is self-developed by Xiaomi Automobile, and integration is also a creative ability."
Wechat-driving AUTO: In fact, how much self-developed things Xiaomi has at this conference is something that can neither be confirmed nor falsified. Because the conclusion of netizens may be just a misunderstanding. The crux of the problem lies in who owns the intellectual property rights of technology. If it is a joint development but the intellectual property belongs to Xiaomi, from the perspective of property rights and law, Xiaomi claims that there is nothing wrong with "self-research", and even from the perspective of public order and good customs in the automobile circle, it is not against it. However, if the external publicity is renamed as "joint development", the shocking effect of publicity will obviously not be achieved, and the personnel of technological subversion will not be established, so "self-research" is necessary.
Wechat-poison tongue technology: self-research in the eyes of netizens and self-research defined by the industry are often not the same thing. Xiaomi’s plan is to explore a rotor material with leading strength with partners, thus developing a brand-new motor with 27,200 rpm. Xiaomi, a die casting machine, is not self-developed. What is really self-developed is the "millet large die casting integrated cluster". In other words, Xiaomi has developed a set of most suitable and efficient production lines, and the die casting machine is also customized by partners according to the needs of this production line. This actually does not prevent Xiaomi from saying that it is self-research.
Netizen: Mainly for poking fun at/not believing in Xiaomi’s self-developed technology, and thinking that Xiaomi encountered the black water army.
Obviously, the motor you bought has to be said to be self-developed, and you are really cheeky.
Just look at the technology of millet blowing, don’t take it seriously, let’s talk about it after seeing the actual effect.
The maximum speed limit is 120. Do you think the motor is fast and useful? Don’t argue about concepts!
Boy, the technology after these years has been pre-developed successfully now.
The precipitation of other big factories for decades and hundreds of years can’t compare with Xiaomi’s research and development in one year?
A certain group stayed up late to prepare for the exam in order to do a background check for Xiaomi Automobile.
Black Xiaomi and those who blow Huawei are the same type of accounts.
Let’s just say that a tree catches the wind. What do you think is the scandal of the dying joint venture?
Now the atmosphere is very funny, saying that Huichuan can’t prove that Xiaomi is self-researched, so Xiaomi is not self-researched. So who said it? Xiaomi said it himself. Do you believe it after Xiaomi said it himself?
Huichuan is quite powerful, with the existence of the top few in China.
Third, the design
1. Appearance is similar to Porsche controversy
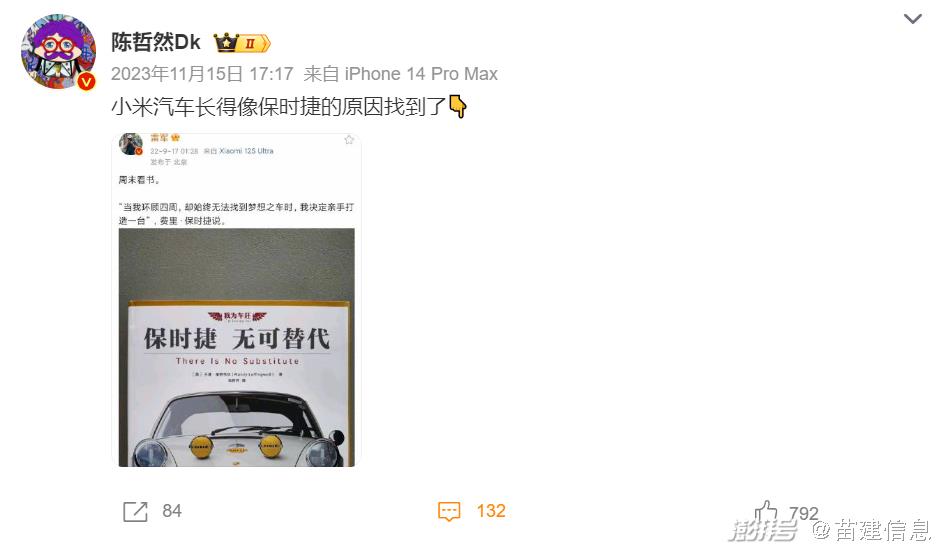
Since the appearance of Xiaomi automobile in the catalogue of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology on November 15, 2023, the appearance of Xiaomi SU7 has been controversial. Because the front face and side of the car are very similar to Porsche, it is ridiculed by netizens that "Mi Shijie" is "not that Porsche can’t afford it, but that Xiaomi is more cost-effective". One plus designer Haoran said that he copied Porsche Paramera, and many self-media published the comparison chart of Xiaomi SU7 and Porsche Taycan. Some cars discovered from the media that Lei Jun Weibo once revealed that he was reading Porsche-related books; Another online picture shows that Xiaomi’s product Xiaoai’s recognition result of Xiaomi SU7 is Porsche. The superposition of all kinds of "coincidences", coupled with Lei Jun’s mention of "comparable to Porsche Tesla" and "the goal is to compete with Porsche" at the press conference, Xiaomi Automobile is caught in a "plagiarism storm".
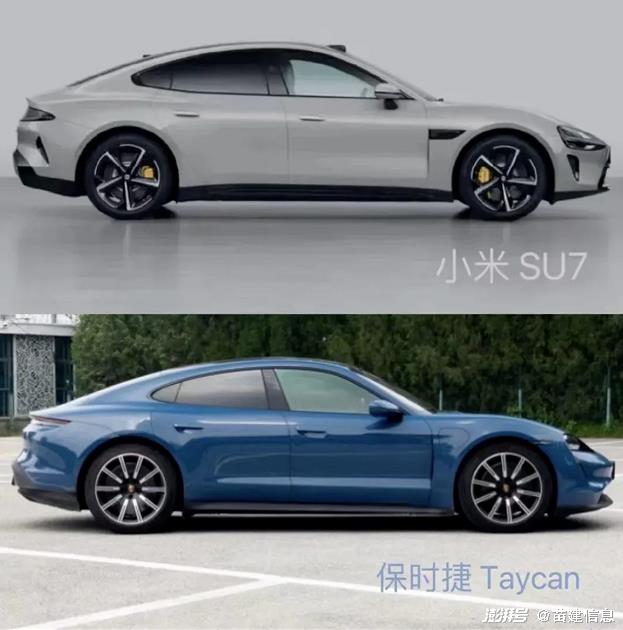

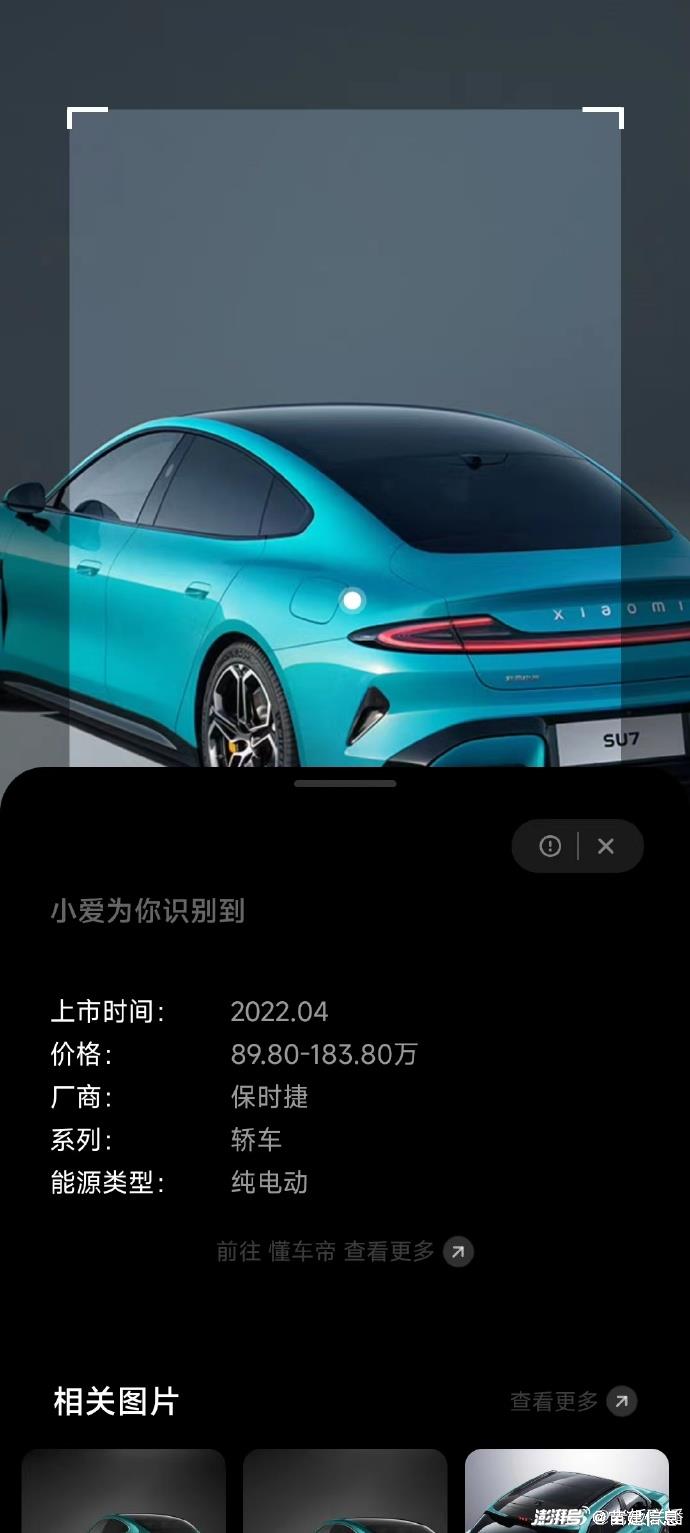
In addition to these doubts and ridicule, there are also many professionals who speak for Xiaomi. Regarding the question of whether Xiaomi automobile plagiarized or borrowed, many disputes helped the outbreak of public opinion.
There is no plagiarism:
Domestic automobile styling design has long bid farewell to the stage of plagiarism. As for what it looks like and what nickname it is, it is the category of the media. Sometimes quite speechless, there is always an angle to black millet; In industrial design, the streamline of coupe should be beautiful and low wind resistance, and it can only look similar, which is the only choice determined by aesthetic and scientific path after industrial design develops to a mature stage.
Ridicule plagiarism:
You don’t understand, this is actually a tribute to Porsche, the predecessor of the industry; Low-key, I think it can rival the aircraft carrier; Because it is comparable, the exterior is copied from Porsche and the interior is copied from Tesla. Combined, it is perfect.
Mention that other car companies are also suspected of plagiarism, implying that sunspots "follow the trend" and "double standard":
I’m curious why many netizens plagiarized Xiaomi’s car because it looks similar to Porsche, but no one said that the car chosen by Huawei is similar to Porsche.
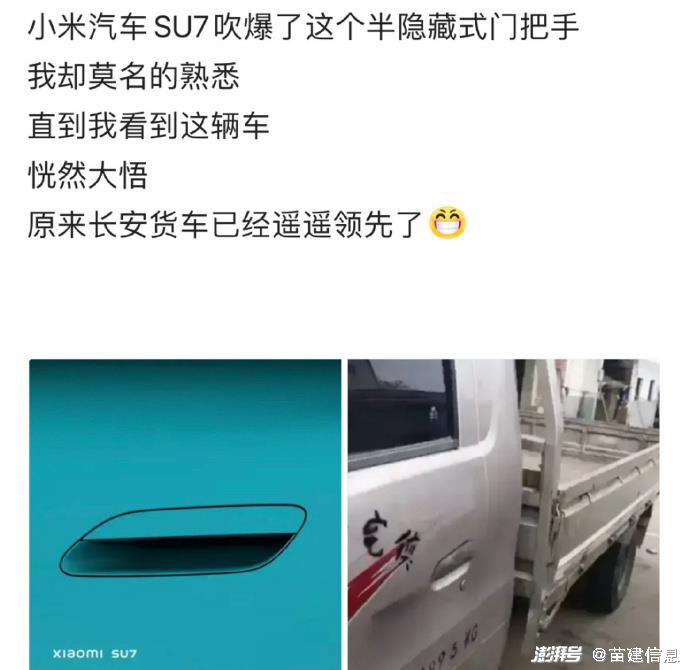
2. Controversy over the design of semi-hidden door handles.
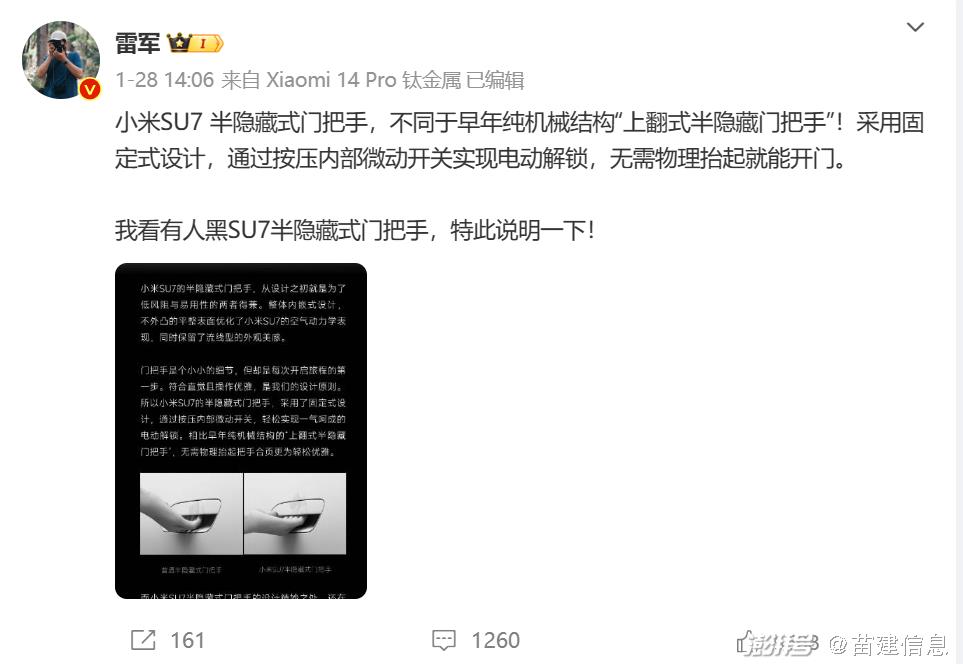
In addition, the conference also announced the patented design of the semi-hidden handle. Its embedded design not only optimizes the aerodynamic efficiency of the vehicle, but also retains the aesthetic feeling of its streamlined appearance. What’s more outstanding is that it skillfully solves the freezing problem in cold weather and avoids the pop-up difficulty that traditional pop-up door handles may encounter. However, some netizens complained that this design was "very familiar", and then Lei Jun also emphasized in Weibo that the semi-hidden door handle was completely different from the early pure mechanical structure "upturned semi-hidden door handle".
3. Other design disputes
In addition, the plum blossom wheel hub, the borderless cobblestone rearview mirror and the 105L front reserve box have also been ridiculed by some netizens that "this design has existed for a long time".
03
Analysis of communication characteristics
1. Price-related topics account for a large proportion, which is the key node to arouse public opinion.
Before the technical conference, Lei Jun revealed in Weibo that "Xiaomi SU7 is a bit expensive", and the topic was on the hot search, and public opinion tended to rise. Then there is the recurring price topic: # Rice flour expects Xiaomi car to be around 300,000 # # Lei Jun said that Xiaomi SU7 has no rivals within 500,000 # # Xiaomi car policy price exposure # # Xiaomi car pricing strategy exposure # and so on.
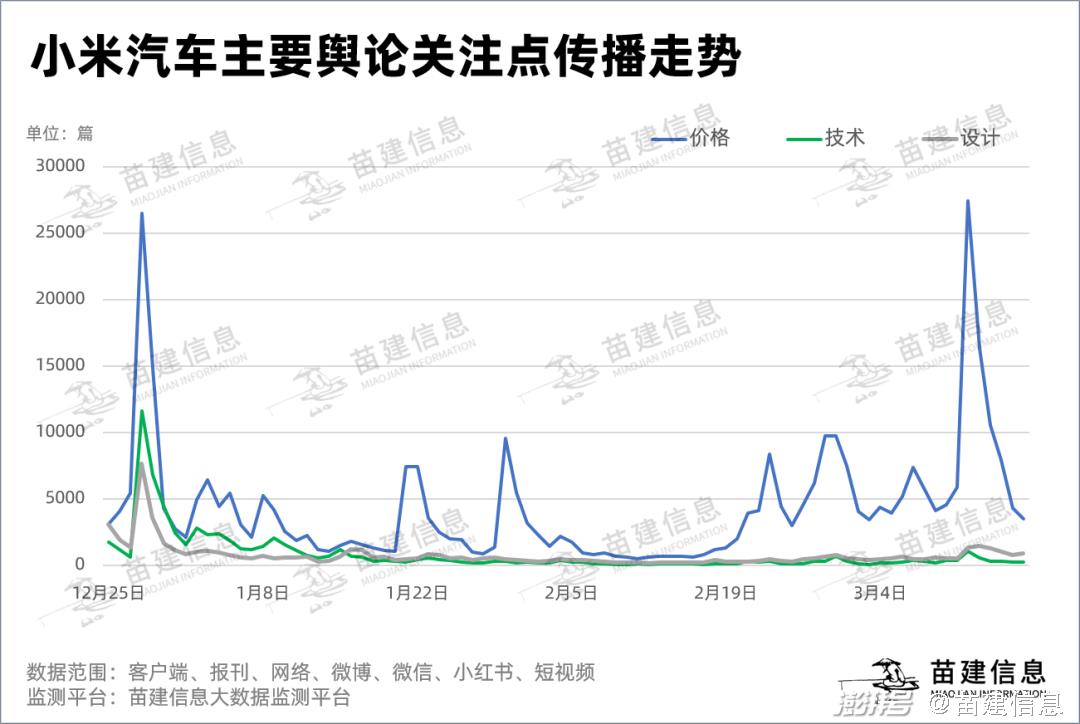
According to the data of Miaojian Information Big Data Monitoring Platform, the high point in the communication trend of Xiaomi Automobile’s price issue almost corresponds to the high point of Xiaomi Automobile’s overall communication trend. The price issue is the main aspect that causes public opinion controversy and is the key for Xiaomi Automobile to maintain a high degree of public concern.
2. Executives and officials frequently voice and refute rumors to promote the spread of topics.
In the early stage of the new car sale, the public opinion field was flooded with false information about price and technology. Lei Jun and Wang Hua, general manager of Xiaomi Group’s public relations department, repeatedly answered questions and rumors in Weibo. The Weibo account "Xiaomi Company Spokesperson" also released rumors about pricing and sales policies, delivery time and technology industry chain. On January 8 -10, Xiaomi Automobile released "Answering 100 Questions from netizens" to comprehensively answer all questions and focus on public concern, which to some extent avoided the persistence of false information on the brand.
According to the display of Miaojian Information Big Data Monitoring Platform, every time executives or officials intervene in the topic, it will cause a certain degree of public opinion fluctuation. On the whole, Xiaomi Automobile still holds a dominant position in the right to speak in public opinion. Although it is riddled with rumors, it has caused some self-media smearing and ridicule by netizens. However, the rapid rumor-dispelling and pre-emptive public relations method not only dispels the doubts of the industry, but also provides a continuous discussion for its own products.
3. The ups and downs of brand reputation are not obvious.
Miaojian Information Big Data Monitoring Platform shows that Xiaomi Automobile has a relatively large amount of sensitive information on the day of the technology conference, the rumor of giving Beijing license, and the extremely high-level executives talking about Xiaomi Automobile at the press conference. In the three months from the technical conference to the official conference, the topic headed by price is still in the discussion stage, and the related negatives are mainly rumors, which have limited practical impact on the brand reputation of Xiaomi Automobile.
04
Public opinion risk judgment
1. Be involved in the "price war" dilemma after pricing is released.
In the year of the Year of the Loong, Tesla took the lead in price reduction, and then BYD made a low price of 79,800 yuan. Changan Automobile, Nezha Automobile and other brands followed suit, and this year’s price war began. On February 27th, the new Extreme Krypton 001 went on the market, with a starting price of 269,000 yuan. Some media claimed that "Extreme Krypton gave Xiaomi a problem". On the day when Xiaomi Automobile announced its pricing, it will inevitably bring certain "fluctuations" to the auto market. For Xiaomi Automobile, whether to follow up the price war may become a hot topic in the market. How to break through in the price knockout is the challenge that Xiaomi is about to face.
2. Repeated marketing, led by price, leads to self-attack.
The topic of manufacturing is Xiaomi’s marketing style in the field of mobile phones. When it is used in Xiaomi cars, it is the product positioning that is close to Porsche, Tesla and other high-end products after frequent price snooping and opening. The price topic was frequently searched, and the executives responded many times. Before the conference, they paid tribute to other car companies and said that they were "comparable to Porsche" …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
3. It is difficult to get rid of labels such as "imitation" and "cottage"
Whether it is the marketing method of the brand or the malicious smear of peers, it has been labeled as "imitating foreign models" since it came out, which can easily deepen the stereotype of the public and thus produce psychological resistance to the brand. In the car sale stage, similar teasing will continue, which will affect short-term sales to some extent. In the long run, whether Xiaomi SU7 can get rid of the negative label with a good enough driving experience, make excellent performance a competitive advantage of the product, and reverse the relatively negative market perception will also be the focus of public opinion.
4. Other negative brands, negative road test and negative test drive affect Xiaomi’s reputation.
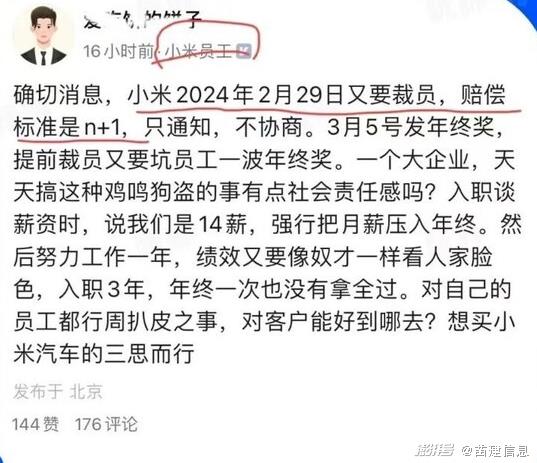
Recently, a Xiaomi employee said on the Internet that Xiaomi will lay off employees on February 29, and "only notice, no consultation" and "no year-end bonus after being laid off", and finally said "think twice about buying a Xiaomi car". On February 3rd, a photo of a suspected collision of Xiaomi SU7 during the road test came out on the Internet, which aroused public concern. Shake consumers’ decision to buy a car. On March 19th, Xiaomi Auto officially responded that the content was maliciously misinterpreted by some accounts, and there was no violation, and it was still communicating with the expressway group on false information. Xiaomi Automobile has attracted much attention. Once the public opinion such as the negative operation of Xiaomi Group, the negative road test of Xiaomi Automobile and the negative test drive experience of new cars in offline outlets occur, it will lead to a decline in its reputation, which will easily affect the marketing process and sales of Xiaomi Automobile.
5. Brand executives’ speeches caused controversy.
Lin Bin, vice president of Netcom Xiaomi, said in a circle of friends, "Driving Xiaomi SU7 from Beijing to Shenzhen office, starting at 7: 30 on Saturday morning and arriving at Shenzhen office at 11: 00 on Monday morning, the whole journey is 2320 kilometers, passing through Wuhan and Guangzhou, and charging for 5 times. (This is a great experience.) This content triggered some speculation about the endurance of Xiaomi SU7 from the media, and concluded that the endurance achievement rate was low. Among them, the self-media account "Chatting Car" only converted electricity consumption by charging times, and the published article was not rigorous, which was complained by Xiaomi Automobile. Some also said from the media that "if it is not full every time, he will definitely explain it clearly in the text. What an important habit it is." Executives’ speeches are often easily amplified and interpreted by the media, and if there is any imprecision, it will easily lead to controversy.
6. Peer-to-peer friends’ speeches caused controversy
Regarding Xiaomi Auto’s tribute to its peers, Yang Xueliang, vice president of Geely, said that "it’s too late". "If people always want to be paid tribute, it’s over, but if people always want to pay tribute to others, there is no promise"; Zhu Ling, vice president of Krypton, also posted a blog suggesting that Xiaomi’s marketing is more and more like health care industry’s, and commented sharply that "the last one who shouted out eco-cars seems to be LeTV mobile phones". On February 27th, at the launch conference of the brand-new Extreme Krypton 001, Extreme Krypton executives talked about Xiaomi Automobile’s "marketing is worth learning", and then # Extreme Krypton executives # boarded the hot search. After the listing of Xiaomi Automobile, the subsequent announcement may also lead to such cynicism and public controversy.